
MobiCom 2020 - FaceRevelio Teaser Video
My research combines system design, signal processing, computer vision, and machine learning methods to investigate security and privacy threats on emerging computing platforms and then proposes methods for securing modern mobile and IoT devices and protecting users’ privacy. Here is a summary of some of the research projects.
We develop authentication systems to enable reliable and secure user and device authentication to protect users’ private information (e.g., contacts, messages, credit card details) on commodity mobile devices and allow secure communication between IoT devices.
FaceRevelio is a novel liveness detection system that protects facial authentication mechanisms on commodity smartphones from spoofing attacks, without requiring effort from the users or any external hardware. It leverages the smartphone screen as a light source and illuminates different portions of the screen with random lighting patterns for a short duration (∼1 second) to simulate multiple lighting conditions. The reflection of the light from the screen is recorded and then used to extract stereo images of the face and its 3D surface through a photometric stereo technique. The reconstructed 3D surface differentiates a real human face from its 2D counterpart and defends against spoofing attacks. This work was presented at MobiCom 2020.

MobiCom 2020 - FaceRevelio Teaser Video
We identify permissionless sensor-based side-channels on mobile devices and show that leakages through these channels seriously threaten users’ privacy.
First, S3 attack demonstrates that modern stylus pencils, a popular accessory used to write, draw, and make selections on smartphones and tablets, have embedded magnets that trigger fluctuations in on-device magnetometer readings when a user interacts with the device using the pencil. We specifically focused on Apple Pencil and showed that a benign malicious app running in the background on a target user’s device can infer what the user is writing from the fluctuations in the permissionless magnetometer sensor’s data. To account for the extensive changes in pencil's position and orientation while a user is writing, through the interplay of signal processing, computer vision, and machine learning techniques, we designed a novel tracking algorithm to track the pencil’s tip movement using the magnetic field data to identify users’ writing. This work was presented at UbiComp 2021.
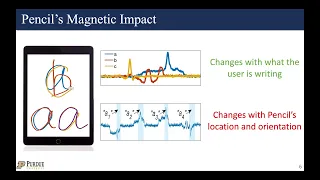
UbiComp 2021 - S3 Presentation
Following S3, we presented a second attack, iStelan, a new side-channel that reveals users’ touch events from permissionless magnetometer sensor data. We exploit the revealed touch event patterns to fingerprint the type of app a user is using, and model touch events to identify users’ touch event types performed on different apps. This work appeared at PoPETs 2023.
In a more recent work, we developed LocIn attack to show that apps’ access to 3D spatial maps collected by mixed reality devices (e.g., HoloLens, iPad Pro with LiDAR) allows adversaries to infer users’ indoor environment, i.e., semantic location, without explicit user permission or any prior knowledge about the user. We introduced a new multi-task learning representation for location inference that unifies the geometric and contextual patterns embedded in the spatial map to infer a user’s location. This work appeared at the USENIX Security Symposium 2023.
Recently, we leveraged our experience in evaluating users’ perception of mobile security and privacy threats through user studies to understand how specific user populations are exposed to digital risks, specifically online hate and harassment.
We specifically focused on online hate and harassment against refugees, a vast population displaced from their home countries due to social and political turmoil. Refugees’ increasing online presence, in order to adapt to their new homes, has heightened their exposure to toxic content attacks, a form of online hate and harassment. Therefore, we investigated the types of toxic content attacks that target refugees and how these attacks affect refugees’ security and privacy actions, goals, and barriers they face in responding to toxic content. Our mixed-method approach of thematic analysis, refugee liaison interviews, and an online survey with refugees revealed diverse assault contexts and how intersecting identities intensify attacks against refugees. This work will appear at the USENIX Security Symposium in 2024.
Within the context of smartphone access control, we also explored the security and usability of Android’s authorization APIs and showed that existing mobile app developers rarely use them correctly to implement secure authorization since using them requires extensive cryptography expertise. To this end, we developed SARA, a secure android remote authorization library to allow developers to integrate secure authorization into their apps easily. We designed and conducted a user study with Android developers to evaluate the usability and practicality of SARA compared to the existing Android APIs and demonstrated that developers could quickly implement secure remote authorization with a few lines of code using SARA. In the spirit of open science, and to ensure our work benefits the entire Android community, we have publicly released SARA [SARA GitHub]. This work led to a collaboration with Google’s Android Security team, and a proposal based on our findings was funded by Google’s ASPIRE Research Award.
We have also investigated how surveillance cameras can digitally associate people in public spaces with their smartphones without knowing the phones’ IP/MAC addresses to enable widespread applications ranging from security surveillance to business intelligence while protecting users’ privacy. We introduced a new communication system between cameras (server) and humans (client) that leverages a person’s context features (e.g., walking velocity, WiFi signal strength around them) as its address. We developed a context feature extraction and selection algorithm that extracts features, from camera videos and users’ smartphone sensor data, capable of distinguishing a specific person from a group of people in the camera view. Through this, a public camera can broadcast a message with a target user’s context address which is only accepted by a user’s phone if its context address matches the phone’s sensor data.
In a recent collaboration, we leveraged insights from statistical learning theory and optimization literature to improve the generalizability and accuracy of collaborative models learnt in federated learning. In later work, we leveraged our understanding of existing federated learning approaches to propose 9 new performance and fairness metrics more suitable for evaluating personalized learning algorithms compared to standard average accuracy metrics.